Diabetes mellitus

Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is a heterogenous group of diseases characterized by a state of chronic hyperglycemia, resulting from diversity of etiologies. The underlying cause is the defective production or action of insulin, a hormone that controls glucose, fat and amino acid metabolism. It is a long term disease with variable clinical manifestations.
Classification
This is the classification by WHO (World health Organization)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Type 1 , insulin dependent
- Type 2 , non-insulin dependent
- Malnutrition related diabetes
- Other types e.g., drug induced
- Impaired glucose tolerance
- Gestational diabetes mellitus
Insulin Dependent Diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
- It is the most severe form of the disease. The onset is usually abrupt, occurs mostly in children, highest incidence in 10-14 years age group.
- It is a catabolic disorder in which the circulating insulin is virtually absent. There is destruction of pancreatic b cells which is immune mediated in 90% of cases and idiopathic in rest of 10%.
- It is lethal until promptly diagnosed and treated.
Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)
- It is much more common than IDDM.
- It is typically gradual in onset occurs mainly in middle aged and elderly.
- It is compatible with long survival given adequate treatment.
Impaired Glucose Tolerance
It is an intermediate state of high risk group individuals – between diabetes mellitus and normality. It can only be detected by oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
What is the main Problem?
Diabetes is an iceberg disease. Currently worldwide cases are around 150 million. This number is predicted to double in 2025. The greatest number of cases being expected in China and India. Unfavorable modification of lifestyle and dietary habits associated with urbanization are believed to be the most important factors for development of diabetes. Prevalence is twice in urban areas than in rural ones.
Epidemiological Determinants
Agent
- The underlying cause is insulin deficiency which is absolute in IDDM and relative in Non IDDM. This may be due to
- Pancreatic disorders
- Defects in formation of insulin
- Destruction of β cells
- Decreased insulin sensitivity
- Genetic defects and auto immunity
Host Factors
Age
It may occur at any age but the prevalence rises steeply with age. The prognosis is worse in younger diabetics who tend to develop complications earlier than older diabetics.
Sex
In some countries male to female ratio is equal. In South East Asia an excess of male diabetics are observed.
Genetic Factors
More important in Non IDDM. Genes involved are HLA-B8, B15, HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR4.
Immune Mechanisms
There is some evidence of cell mediated and humoral activity against islet cells.
Obesity
Risk is related to both degree and duration of obesity.
Maternal Diabetes
Off springs of diabetic pregnancies are often large and heavy at birth, tend to develop obesity in childhood and tend to develop type 2 diabetes at an earlier age.
Environmental Risk Factors
- Sedentary life style is an important risk factor, lack of exercise may alter the interaction between insulin and its receptors.
- Highly saturated fat intake has been associated with a higher risk of glucose intolerance.
- Malnutrition in early childhood may result in partial failure of β cell function.
- Excessive intake of alcohol may damage the pancreas and liver.
- Chemical Agents which are toxic to pancreas.
Screening for Diabetes
Urine Examination
- It is done 2 hours after meal. Most common test.
- All those with glycosuria are considered diabetics unless proved by OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test).
- Glucose is found in urine in severe diabetics but is absent in milder forms and such cases are likely to be missed by urine test. This is lack of sensitivity.
- Further glycosuria may be found in perfectly normal giving rise to false positive cases. So, urine testing is not appropriate in case finding.
Blood Sugar Testing
Screening Tests
| Screening Test | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|
40% | 90% |
|
70% | 75% |
|
75% | 80% |
Diagnostic Tests
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
| Diagnostic Test | Fasting | 2 hours after Load |
|
>108 mg/dl | <140 mg/dl |
|
108-126 mg/dl | 140-198 mg/dl |
|
>126 mg/dl | >198 mg/dl |
Prevention
Primary Prevention
Population Strategy
- The scope of primary prevention of non IDDM is limited on the basis of current knowledge and is probably not appropriate
- However the prevention of NIDDM can be done by elimination of environmental risk factors.
- Measures are maintenance of normal body weight, physical exercise adequate protein intake, high dietary fiber and avoidance of sweet foods.
High Risk Strategy
- Avoidance of sedentary life style
- Avoidance of over nutrition and correction of obesity.
- Avoidance of alcohol.
- Avoidance of diabatogenic drugs.
- Reduction of factors that lead to atherosclerosis.
Secondary Prevention
- When diabetes is detected, it must be adequately treated.
- The aims are
- To control blood sugar levels.
- To maintain ideal body weight.
Treatment
- Diet alone.
- Diet with oral antidiabetic drugs.
- Diet with insulin.
Monitoring
- Routine checking of blood sugar levels , urine for proteins and ketones , blood pressure, visual acuity and weight
- Examination of feet for sensations.
- Checking HbA1C at 6 monthly interval.
Self-care
Patent should be emphasized upon need of blood sugar control, stick to the diet plan and monitor blood sugar levels at home.
Tertiary Prevention
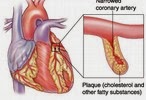
- Diabetes is a major cause of disability through its complications e.g., blindness, kidney failure, coronary thrombosis, gangrene of the lower extremities etc.
- The main objective at tertiary level is to organize diabetic clinics for diagnosis and management.
- It has also been recommended that local and national registries for diabetics should be established.
Identification Card
- The patient should carry an identification card showing his name, address, telephone number (if any) and the details of treatment he is receiving.
- In short he must have the working knowledge of diabetes.
Obesity
It may be defined as an abnormal growth of adipose tissue due to an enlargement of fat cells or an increase in the fat cell number or a combination of both. Overweight is usually due to obesity but can arise from other causes such as abnormal muscle development or fluid retention. However obese individuals differ not only in the amount of fat but also in the distribution of fat.
Prevalence
- Obesity is the most prevalent form of malnutrition. It is prevalent in both developed and developing countries affecting children as well as adults.
- It affects 20-40% of adults and 10-20% of children in developed countries.
- It is one of the most common contributors to ill health. In industrialized countries it is primarily due to reduced physical activity rather than changes in food intake.
What is the main problem?
Obesity is a key factor in natural history of other chronic and non-communicable diseases. The adverse effects are hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and glucose intolerance while coronary heart disease and complications of diabetes such as renal failure begin to emerge several years later.
Epidemiological Determinants
Age
It can occur at any age and generally increases with age. Infants with excessive weight gain have an increased incidence of obesity in later life.
Sex
Women generally have higher rate of obesity than men. It has been claimed that women’s BMI increases with successive pregnancies.
Genetic Factor
Studies have shown that genetic factor has a role in etiology of obesity.
Physical Activity
- There is convincing evidence that regular exercise protects against unhealthy weight gain.
- Whereas sedentary lifestyle and inactive recreation such as watching television promote it.
- Physical inactivity may cause obesity, which in turn restricts activity. This is a vicious circle.
Socio Economic Status
- There is clear inverse relationship between socio economic status and obesity.
- Eating habits
- Eating in between meals, preference to sweets and fatty foods .a diet containing more energy than needed may lead to prolonged postprandial hyperlipidemia and deposition of triglycerides in adipose tissue resulting in obesity.
Psychological factors
Over eating may be a symptom of depression, anxiety, frustration and loneliness in childhood as it is in adult life.
Endocrine Factors
Cushing syndrome or growth hormone deficiency.
Alcohol
Alcohol intake is directly associated with obesity.
Education
Inverse relationship between education and obesity.
Smoking
Use of tobacco lowers body weight.
Drugs
Corticosteroids, contraceptives, insulin and β blockers can promote weight gain.
Use of BMI to Calculate Obesity
- It is the simple index of weight for height. It is commonly used to classify underweight, over weight and obesity in adults.
- It is defined as weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters
- BMI = Weight in Kg / (Height in meter)2
WHO Classification of Obesity
| Classification | BMI | Risk of Co-morbidity |
|
<18.5 | Low |
|
18.5-24.9 | Average |
Pre obese Obese class I Obese class II Obese class III |
>2525-29.930-34.935-39.9>40 | IncreasedModerateSevereVery SevereVery Severe |
Assessment of Obesity
- There are various methods of assessment of obesity.
- BMI (Body Mass Index)
- Ponderal index
- Broca index (Height in cm-100 e.g., 160-100=60 Kg
- Lorentz formula
- Corpulance index
Skinfold Thickness
A large proportion of total body fat is located under the skin. It is taken at 4 sites mid triceps, biceps, subscapular and suprailiac region .the sum of all 4 should be less than 40mm in boys and less than 50 mm in girls.
Waist Circumference and Waist Hip Ratio
Waist circumference is simple and correlates strongly with BMI. Waist hip ratio is an approximate index of total body fat.
Hazards of Obesity
Greatly Increased Risks
- Non-insulin dependent Diabetes mellitus
- Gall Bladder Disease
- Sleep Apnea
- Dyslipidemia
- Breathlessness
Moderately Increased Risks
- Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
- Gout
- Hypertension
- Hyperuricemia
- Osteoarthritis
Slightly Increased Risks
- Breast Cancer
- Colorectal carcinoma
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Reproductive hormonal abnormalities
- Low backache
- Sterility
- Chronic Obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Prevention and Control
- Weight control, BMI of 18.5-24.9kg/m2
- Dietary Changes
- Proportion of energy dense food such as simple carbohydrates and fats should be reduced.
- The fiber content in the diet should be increased.
- Adequate amount of essential nutrients in low energy diet should be ensured.
- Increased physical activity
- Appetite suppressing drugs have been tried. They are generally inadequate to control weight in massively obese individuals.
- Surgical treatment.
- Gastric bypass, gastroplasty and jaw wiring have been used to eliminate the eating of solid foods with limited success.
For downloading the article in PDFs format, click on the following button;
Other Topics |













Leave a Reply