Obesity

Obesity
Obesity may be defined as an abnormal growth of adipose tissue due to an enlargement of fat cells or an increase in the fat cell number or a combination of both. Overweight is usually due to obesity but can arise from other causes such as abnormal muscle development or fluid retention. However obese individuals differ not only in the amount of fat but also in the distribution of fat.
Prevalence
- Obesity is the most prevalent form of malnutrition. It is prevalent in both developed and developing countries affecting children as well as adults.
- It affects 20-40% of adults and 10-20% of children in developed countries.
- It is one of the most common contributors to ill health. In industrialized countries it is primarily due to reduced physical activity rather than changes in food intake.
What is the main problem?
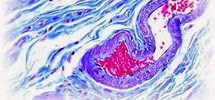
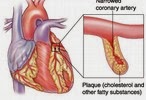
Obesity is a key factor in natural history of other chronic and non-communicable diseases. The adverse effects are hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and glucose intolerance while coronary heart disease and complications of diabetes such as renal failure begin to emerge several years later.
Epidemiological Determinants
Age
It can occur at any age and generally increases with age. Infants with excessive weight gain have an increased incidence of obesity in later life.
Sex
Women generally have higher rate of obesity than men. It has been claimed that women’s BMI increases with successive pregnancies.
Genetic Factor
Studies have shown that genetic factor has a role in etiology of obesity.
Physical Activity
- There is convincing evidence that regular exercise protects against unhealthy weight gain.
- Whereas sedentary lifestyle and inactive recreation such as watching television promote it.
- Physical inactivity may cause obesity, which in turn restricts activity. This is a vicious circle.
Socio Economic Status
- There is clear inverse relationship between socio economic status and obesity.
- Eating habits
- Eating in between meals, preference to sweets and fatty foods .a diet containing more energy than needed may lead to prolonged postprandial hyperlipidemia and deposition of triglycerides in adipose tissue resulting in obesity.
Psychological factors
Over eating may be a symptom of depression, anxiety, frustration and loneliness in childhood as it is in adult life.
Endocrine Factors
Cushing syndrome or growth hormone deficiency.
Alcohol
Alcohol intake is directly associated with obesity.
Education
Inverse relationship between education and obesity.
Smoking
Use of tobacco lowers body weight.
Drugs
Corticosteroids, contraceptives, insulin and β blockers can promote weight gain.
Use of BMI to Calculate Obesity
- It is the simple index of weight for height. It is commonly used to classify underweight, over weight and obesity in adults.
- It is defined as weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters
- BMI = Weight in Kg / (Height in meter)2
WHO Classification of Obesity
| Classification | BMI | Risk of Co-morbidity |
|
<18.5 | Low |
|
18.5-24.9 | Average |
Pre obese Obese class I Obese class II Obese class III |
>25-29.930-34.935-39.9
>40 |
IncreasedModerate
Severe Very Severe Very Severe |
Assessment of Obesity
- There are various methods of assessment of obesity.
- BMI (Body Mass Index)
- Ponderal index
- Broca index (Height in cm-100 e.g., 160-100=60 Kg
- Lorentz formula
- Corpulance index
Skinfold Thickness
A large proportion of total body fat is located under the skin. It is taken at 4 sites mid triceps, biceps, subscapular and suprailiac region .the sum of all 4 should be less than 40mm in boys and less than 50 mm in girls.
Waist Circumference and Waist Hip Ratio
Waist circumference is simple and correlates strongly with BMI. Waist hip ratio is an approximate index of total body fat.
Hazards of Obesity
Greatly Increased Risks
- Non-insulin dependent Diabetes mellitus
- Gall Bladder Disease
- Sleep Apnea
- Dyslipidemia
- Breathlessness
Moderately Increased Risks
- Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
- Gout
- Hypertension
- Hyperuricemia
- Osteoarthritis
Slightly Increased Risks
- Breast Cancer
- Colorectal carcinoma
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Reproductive hormonal abnormalities
- Low backache
- Sterility
- Chronic Obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Prevention and Control
- Weight control, BMI of 18.5-24.9kg/m2
- Dietary Changes
- Proportion of energy dense food such as simple carbohydrates and fats should be reduced.
- The fiber content in the diet should be increased.
- Adequate amount of essential nutrients in low energy diet should be ensured.
- Increased physical activity
- Appetite suppressing drugs have been tried. They are generally inadequate to control weight in massively obese individuals.
- Surgical treatment.
- Gastric bypass, gastroplasty and jaw wiring have been used to eliminate the eating of solid foods with limited success.
For downloading the article in PDFs format, click on the following button;
Other Topics |













Leave a Reply